Information on basic methods
of hair transplantation
The first written record of successful hair transplantation to treat baldness in humans was published in 1822 in Wurzburg, Germany-181 years ago. A medical student named Diffenbach described experimental surgery performed by himself and his surgeon mentor Professor Dom Unger in animals and in humans. They successfully transplanted hair from one area of a patient’s scalp to another area.
The modern surgical techniques of hair transplantation were first developed in Japan in the 1930s and 1940s, but did not come to attention outside of Japan until after World War Two. In 1939, Dr. S. Okuda, a Japanese dermatologist, described the use of full-thickness grafts of hair-bearing skin from hair-bearing areas to hairless areas to correct hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows and upper lip. While most of the 200 patients he reported were treated for traumatic alopecia, his technique was almost identical to that first reported in the United States in 1959 to treat androgenic alopecia. Other Japanese surgeons reported successful hair transplantation to areas of the body other than the scalp throughout the 1940s and 1950s; as with Dr. Okuda’s reports, these were written in Japanese and were not seen outside Japan for many years.
Till the 1990s world knew only invasive hair transplant surgery and by the end of the 20th century there were discovered minimally invasive transplantation techniques. Hair transplantation available in three ways:
Hair transplant methods
FUT the surgery with excision of the skin flap on the head
FUE MACHIN the seamless surgery with the formation of scar tissue
HFE = FUE MANUAL completely non-invasive procedures without sutures and the scar tissue
Instruments.
The technology
FUT
the surgery with excision of the skin flap on the head
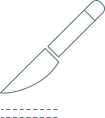
Incisions: scalpel use.
The excised strip
is about 10-25 cm in size.
Grafts are formed from the extraction skin flap from the donor area. Their implantation is performed in the canals formed by the surgeon in the recipient area.
FUE MACHIN
the seamless surgery with the formation of scar tissue.
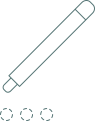
Tiny holes: Punch machine
grafts are
1,5–5,0 mm length.
Group of methods combined follicular units extraction without the incision on the back of the head (in the donor area).
HFE
completely non-invasive procedures without sutures and the scar tissue.
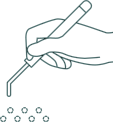
Micro holes:
instruments
(micro punch and implanter pen)
manual hair setting.
grafts are
0,8 mm length.
Transplants present individual follicles or micro follicle units (only 2-3 follicles), extracted via the micro punch from the donor area. Seized follicles implanted in the baldness zone by the micro implanter.
Side effects of hair transplant surgery


In general FUT procedures use the scalpel / blade opening method of follicle placement. This means that the doctor is required to make an opening in the thinning area of the scalp with a scalpel and then place the follicles / hairs with a forceps (tweezers). This does not allow the doctor to control the angle of the hairs placed and there is potentially scarring in this area due to the placement tools used.
Up to 30% of the donor strip area can be damaged during the extraction and also at the stage of cutting into grafts. After the extraction stitches required.
Availability unsightly scar that remains for life, which does not allow to have short hairstyles In extreme cases, may be damage nerve endings and numb, which may be accompanied by headaches.
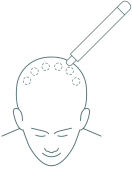

Without following the natural direction of hair growth. The presence of unsightly scars that remain for life, which does not allow short haircuts. In extreme cases, may be damage nerve endings and numb which may be accompanied by headaches.
Traumatic postoperative facial swelling that lasts up to 14 days.
Postoperative scars across part of the occipital part of the head (such as "checkerboard") that will last a lifetime.


Less invasive method = no scars, no stitchies, no pain and minimal skin damage
The hfe technique allows us to place follicles by the use of implanter at the correct angle, direction and depth without creating scars.
Skin sensitivity maintained at 100 %.
The surgical duration
4 hours
8 hours
4 hours
The healing of donor area
4-12 weeks
2-4 weeks
Up to 2 weeks, micro-wounds in the donor area heal within 3-5 days
The public appearance
6 months
2 months
3-4 weeks
Sport activities
Two months after
One months after
One week after
The hair density after the transplant
30-40 follicles per cm2
50–60 follicles per cm2
Up to 80 follicles per cm2
The natural look
Unnatural hair tilt angle
Unnatural hair tilt angle
Natural hair tilt angle
The repeated hair extraction from donor area
Performing repeated procedures possible, but not more than 2-3 times .
Performing repeated procedures impossible or difficult.
If required possibility of multiple processes.
Survival rate of the grafts transplanted
About 60%
80–90%
Up to 98%
The skin damage
Significant: excision of the skin flap and scar in the recipient area.
Significant: presence of unsightly small scars remain forever.
Non- significant: small wounds after hair transplantation healing in a few days, without leaving any trace.
The donor area
The back of the head
The back of the head
The back of the head

